Potential Complications Of Total Parenteral Nutrition
Total parenteral nutrition can provide an individual with the necessary nutritional support and provision of therapeutic nutrients to maintain or restore optimal nutrition status and health. PN should be used for the shortest period possible and oral or.

Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition Download Table
Nutritional support posthematopoietic stem cell transplantation HSCT with total parenteral nutrition TPN or nasogastric tube feeding NGT in pediatric patients is associated with benefits and risks.

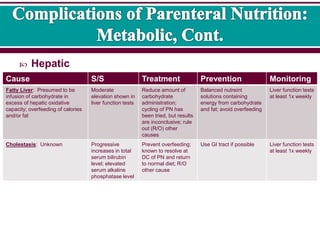
Potential complications of total parenteral nutrition. Parenteral nutrition has been shown to improve clinical outcome in patients with malnutrition and intestinal tract dysfunction. Several clinical and pathological entities including steatosis steatohepatitis cholestasis and cholelithiasis have been commonly linked to TPN. Glucose overload can cause an osmotic diuresis or stimulate insulin secretion which in turn promotes extracellular to intracellular shifts of potassium and phosphorous.
The estimated BMR value may be multiplied by a number that corresponds to the individuals activity level. Continued technological improvements in the quality of nutritional formulations and techniques for parenteral administration have resulted in a major improvement in patient care. An infection in your bloodstream known as sepsis is very dangerous and can be fatal.
Possible complications are similar to those seen in patients with diabetes mellitus. Parenteral nutrition gives a person the nutrients and calories they need through a vein instead of through eating. The American Journal of Surgery 1986.
Author J P Knochel. Glucose load exceeds endogamous insulin secretion. As with any treatment its possible for complications to happen.
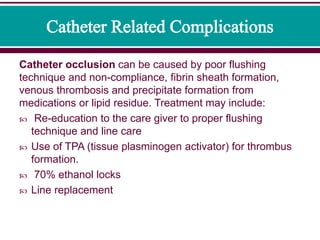
While PN is life-sustaining it associated with a host of complications including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD and central line-associated bloodstream infections CLASBIs which carry a high morbidity and mortality and pose a burden to the healthcare system. Knochel Dallas Texas USA Dallas Texas USA Continued technological improvements in the quality of nutritional formulations and techniques for parenteral administration have resulted in a major improvement in patient care. Infection occurring around the catheter access point to the vein is the most significant complication of parenteral nutrition.
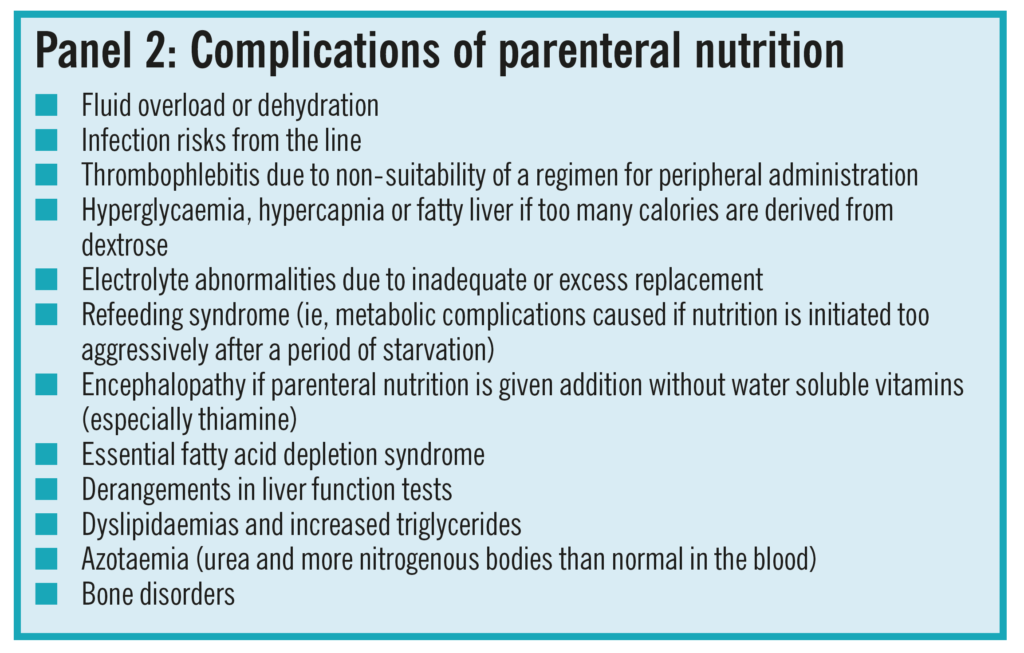
Complications of parenteral nutrition. Possible complications associated with TPN include. Total Parenteral Nutrition bypasses the digestive system by dripping a nutritionally adequate hypertonic solution containing glucose protein hydrolysates minerals and vitramins.
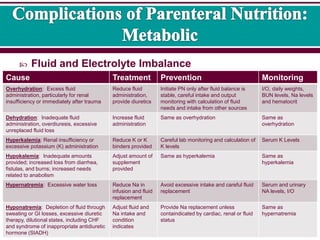
A complication was considered. Men BMR 10 weight in kg 625 height in cm 5 age in years 5. Fluid and electrolyte imbalances.
Complications of total parenteral nutrition Kidney Int. Early recognition of the signs and symp-toms of complications and knowledge of the available pharmacologic and nonphar-macologic therapies are essential to prop-er management. We retrospectively reviewed the indication of TPN use in our pediatric HSCT patients and its impact on survival and possible related complications.
Dehydration and electrolyte Imbalances. Fluid overload can cause congestive heart failure particularly in elderly and debilitated patients. Parenteral Nutrition Total adverse effects Phosphates blood Phosphorus Metabolism Disorders etiology.
Assessment Tools and Guidelines Jay M. O lean body mass o support the structure and function of the organs o prevent nutrient deficiencies o do no harm It is more common to. Complications Associated with Total Parenteral Nutrition.
Parenteral nutrition can be given temporarily or for a longer time. Parenteral nutrition PN is essential to the practice of neonatology. The general goals are to support.
The ability to provide all necessary nutrients by intravenous infu-sion so-called total parenteral nutrition TPN has sustained life and growth in patients who otherwise would have died. Parenteral nutrition complications can be divided into mechanical related to vascular access septic and metabolic. The use of parenteral nutrition is not without risk of serious complications.
The likelihood of hyperglycaemia induced complications may depend on. With total parenteral nutrition usually called TPN a person gets 100 of the nutrition they need each day through a vein. Possible complications associated with TPN include.
Refeeding Syndrome Before initiating parenteral nutrition the patient should be assessed for the risk of. The ability to provide all necessary nutrients by intravenous infusion so-called total parenteral nutrition TPN has sustained life and growth in patients who otherwise would have died. However this is uncommon.
Parenteral nutrition is considered a high-risk nutrition therapy as there are many potential complications that may arise when parenteral nutrition is used. The relationships between various hepatobiliary disorders and the administration of total parenteral nutrition TPN were reviewed and in particular the role of TPN in their pathogenesis was critically evaluated. A polemic point of view expressed Death by parenteral nutrition TPN total poisonous nutrition.
Tritional formulations and techniques for parenteral administra-tion have resulted in a major improvement in patient care. Add insluin to parenteral solution or give subcutaneously. Editorial Review Complications of total parenteral nutrition James P.
Our aim is to review the specific complications of TPN. BackgroundAims Total parenteral nutrition TPN has proven a tremendous advance in all disciplines in medicine but itself introduces a spectrum of possible complications related to both the parenteral nutritional solution as well as the technique of intravenous delivery. Materials and methods This article.
All hospitalized patients except infants a total of 1647 patients who received central venous TPN solutions at UCDMC from 1981 through 1985 were studied to determine the incidence of complications from the use of TPN. Metabolic complications of total parenteral nutrition. The Different Types of Feeding Tubes.
Total Parenteral Nutrition Definition Total parenteral nutrition TPN is a way of supplying all the nutritional needs of the body by bypassing the digestive system and dripping nutrient solution directly into a vein. Metabolic Complications of Parenteral Nutrition. The most important complication of nutritional support is the failure to achieve the desired goals because of inadequate monitoring.
Other potential complications of parenteral nutrition include. Complications of parenteral nutrition. Advance rate slowly do not increase until hyperglycemia is controlled.
The resulting number is the approximate daily kilocalorie intake to maintain current body weight. And response to nutritional support are es-sential in avoiding these complications. The risk of infectious complications is increased due of venous access for PN.
Thrombosis blood clots Hyperglycemia high blood sugars Hypoglycemia low blood sugars Infection. Complications of total parenteral nutrition.
3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition

Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition Therapy Download Table
Parenteral Nutrition In Adults The Basics The Pharmaceutical Journal

Table Iii From Total Parenteral Nutrition For Premature Infants Practice Aspects Semantic Scholar
3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition

Pdf Enteral And Parenteral Nutrition In The Perioperative Period State Of The Art
3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition

3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition

Liver Dysfunction Associated With Parenteral Nutrition What Are The Options Semantic Scholar
Post a Comment for "Potential Complications Of Total Parenteral Nutrition"