Hepatobiliary Complications Of Total Parenteral Nutrition
Total Parenteral Nutrition bypasses the digestive system by dripping a nutritionally adequate hypertonic solution containing glucose protein hydrolysates minerals and vitramins. Hepatobiliary complications associated with total parenteral nutrition.

Liver Dysfunction Associated With Parenteral Nutrition What Are The Options Semantic Scholar
Abnormalities of liver function tests in patients receiving short term PN are usually transient but in individuals receiving long term PN substantial liver damage and ultimately end stage liver disease may occur.

Hepatobiliary complications of total parenteral nutrition. Hepatic complications of total parenteral nutrition Am J Med. The relationships between various hepatobiliary disorders and the administration of total parenteral nutrition TPN were reviewed and in particular the role of TPN in their pathogenesis was critically evaluated. Hepato-biliary disturbances occurring during total parenteral nutrition TPN can be considered as the major secondary metabolic complication of this therapy.
Total parenteral nutrition has showed his efficacy in severe digestive diseases. All these hepatobiliary complications are more likely to occur after long-term total parenteral nutrition but they seem to be less frequent andor less severe in patients who are also. Hepatobiliary complications of total parenteral nutrition.
Rhythm duration and nutritional regimen of TPN as well as the underlying disease of patients may play a role in the pathogenisis and prevalence of hepatobiliary complications. Aim of this study is to report hepato biliary complications in 200 adult patients mean age 53 years treated between 1979 and 1988. Aim of this study is to report hepato biliary complications in 200 adult patients mean age 53 years treated between 1979 and 1988.
Fein BI1 Holt PR. Hepatobiliary complications of total parenteral nutrition. Continued technological improvements in the quality of nutritional formulations and techniques for parenteral administration have resulted in a major improvement in patient care.
In 1971 Paden et al. Several clinical and pathological entities including steatosis steatohepatitis cholestasis and cholelithiasis have. Infants manifest primarily intrahepatic.
Hepatobiliary complications of hypoalimentation and parenteral nutrition PN are widely recognised. Well-described parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD has been known to be a complication of TPN used long term over 14 days. Total parenteral nutrition TPN has become an important tool in the management of acutely ill patients and in patients unable to tolerate oral nutrition.
The ability to provide all necessary nutrients by intravenous infusion so-called total parenteral nutrition TPN has sustained life and growth in patients who otherwise would have died. Inducing positive nitrogen balance and weight gain in patients fed exclusively parenterally was documented first by Dudrick et al. Hepatobiliary complications of total parenteral nutrition.
Three types of hepato biliary complications. It is remarkable that glutamine-free total parenteral nutrition over a 2-months period does not result in distinctive changes in mucosal morphology. Hypoalimentation includes conditions such as anorexia nervosa AN obesity malnutrition and liver disease following bariatric surgery.
However infections metabolic and hepato biliary complications can appear. Experimental and clinical studies indicate that hepatic steatosis is a. In general the incidence of total parenteral nutrition-related hepatobiliary complications has been reported to be very high ranging from 20 to 75 in adults.
However it is concluded that it is often difficult to extricate the effects of TPN on hepatobiliary function from many other hepatotoxic factors that may be operative in these patients. Evidence of hepatic dysfunction clinically chemically and morphologically and biliary-tract abnormalities is common in patients receiving TPN. The relationships between various hepatobiliary disorders and the administration of total parenteral nutrition TPN were reviewed and in particular the role of TPN in their pathogenesis was critically evaluated.
In general the incidence of total parenteral nutrition-related hepatobiliary complications has been reported to be very high ranging from 20 to 75 in adults. Micronutrient deficiencies vitamin and minerals As renowned nutrition experts we lead pioneering research that helps patients on TPN. Several clinical and pathological entities including steatosis.
Treatment of the underlying condition causing hypoalimentation can result in an improvement in liver dysfunction. The relationships between various hepatobiliary disorders and the administration of total parenteral nutrition TPN were reviewed and in particular the role of TPN in their pathogenesis was critically evaluated. The entity might present as hepatocellular injury fatty liver steatonecrosis intrahepatic cholestasis acalculous cholecystitis or cholelithiasis.
Total parenteral nutrition is now widely used in the treatment of nutritional depletion. Several clinical and pathological entities including steatosis steatohepatitis cholestasis and cholelithiasis have been commonly linked to TPN. 1 first recognized hepatobiliary complications in infants on total parenteral nutrition TPN.
Lukes-Roosevelt Hospital Center New York New York. PNALD is characterized by inflammation causing cholestasis steatosis resulting in. Total parenteral nutrition has showed his efficacy in severe digestive diseases.
Parenteral nutrition PN is essential to the practice of neonatology. 1Division of Gastroenterology St. Clinical epidemiological data indicate that total parenteral nutrition TPN may be associated with a.
Although the benefits of this treatment are obvious there are various hepatobiliary complications. Among problems that persist in the use of this technique the development of hepatic abnormalities has received increasing attention. While PN is life-sustaining it associated with a host of complications including parenteral nutrition-associated liver disease PNALD and central line-associated bloodstream infections CLASBIs which carry a high morbidity and mortality and pose a burden to the healthcare system.
Total parenteral nutrition can provide an individual with the necessary nutritional support and provision of therapeutic nutrients to maintain or restore optimal nutrition status and health. Liver dysfunction is common in individuals receiving parenteral nutrition PN and particularly in neonates and infants. Dehydration and electrolyte Imbalances.
Hepatobiliary complications associated with total parenteral nutrition Introduction. Possible complications associated with TPN include. Thus whereas considerable evidence exists to support a role fro carbohydrate or calorie excess.
Thrombosis blood clots Hyperglycemia high blood sugars Hypoglycemia low blood sugars Infection. However infections metabolic and hepato biliary complications can appear. All these hepatobiliary complications are more likely to occur after long-term total parenteral nutrition but they seem to be less frequent andor less severe in patients who are also.
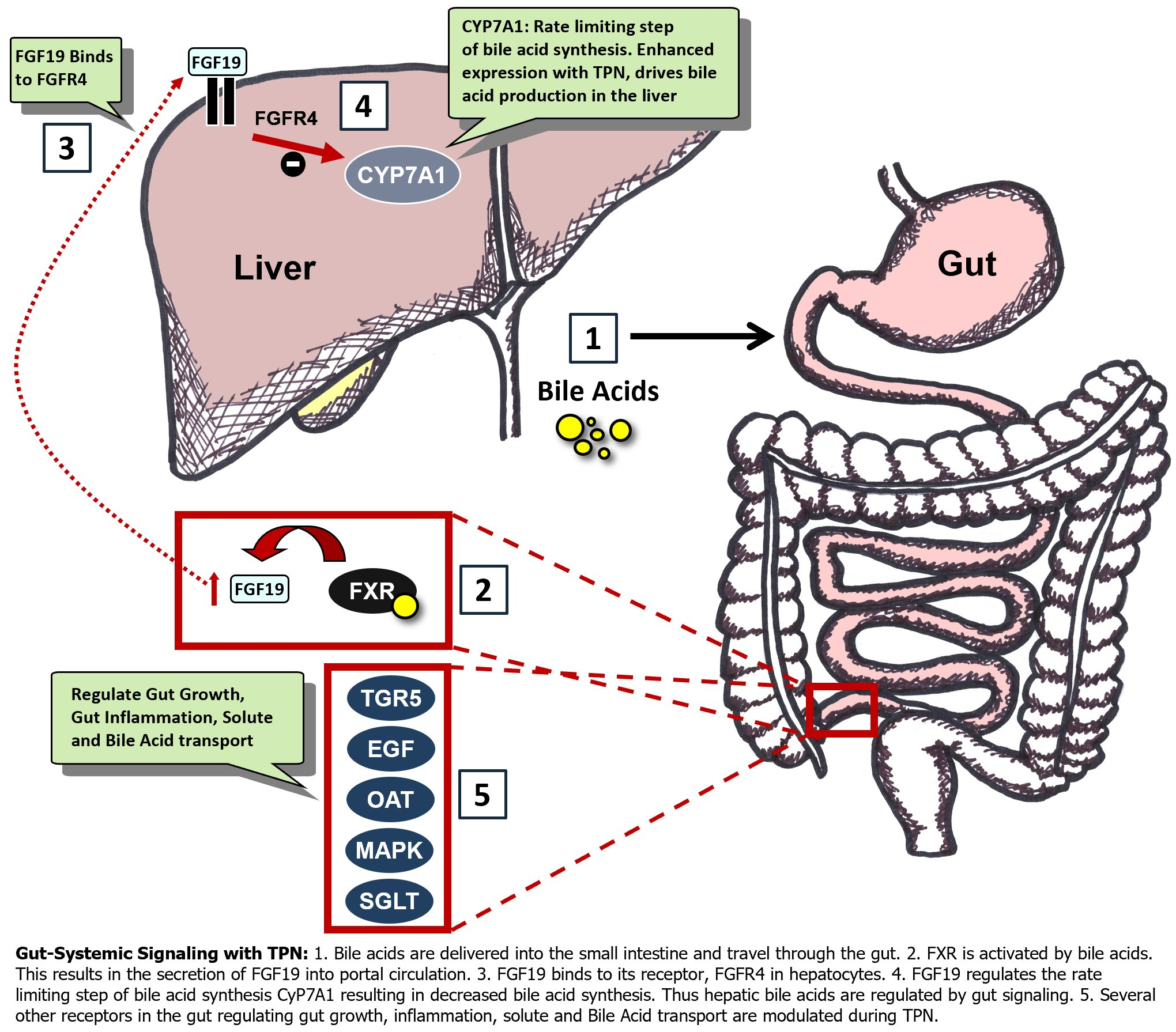
Nutrients Free Full Text Impaired Gut Systemic Signaling Drives Total Parenteral Nutrition Associated Injury Html

Management Of Parenteral Nutrition Associated Liver Disease Download Table
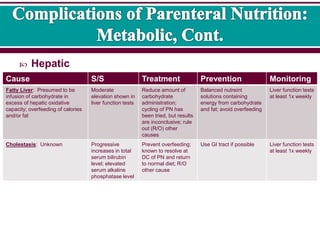
3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition

Pdf Total Parenteral Nutrition Related Gastroenterological Complications
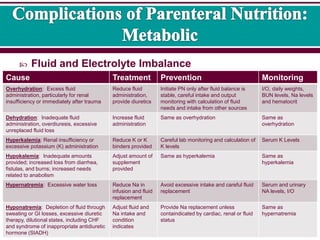
3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition
Pdf Complications Of Long Term Home Total Parenteral Nutrition Their Identification Prevention And Treatment

Liver Dysfunction Associated With Parenteral Nutrition What Are The Options Semantic Scholar

3 Complications Of Parenteral Nutrition

Liver Dysfunction Associated With Parenteral Nutrition What Are The Options Semantic Scholar
Post a Comment for "Hepatobiliary Complications Of Total Parenteral Nutrition"